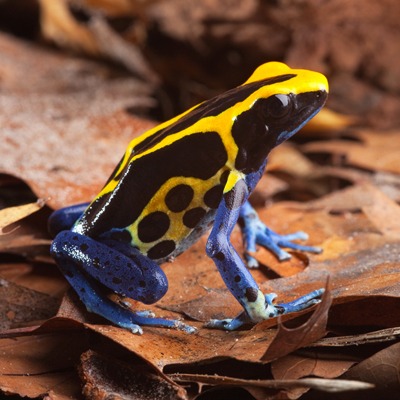

About Yellow and Blue Poison Dart Frog
The yellow and blue poison dart frog is very active during the daytime and moves with short leaps. This species is bold, aggressive, and very territorial, especially males who are known to fight over territories. However, both sexes are known to defend their territories from frogs of the same species as well as those of other species. The aggressive behavior usually consists of calling, chases, and wrestling. Wrestling usually occurs between those of the same sex but can also occur between males and females.
Habitat
These frogs are found in the southern part of South America. They live in humid and warm climates and prefer dark, moist environments, living on the rainforest floor and tree roots near water sources. Though they typically stay on the ground, they have been found in trees as high as 16 feet!
Diet
Yellow and blue poison dart frogs’ diet consists of ants, beetles, flies, mites, spiders, termites, maggots, and caterpillars.
Family Life
They are solitary animals, interacting with each other only during territorial fighting and breeding. Females usually produce between five to ten offspring per clutch. They lay eggs out of the water and then the tadpoles are carried by the males to puddles where they develop further.
Conservation Status
The conservation status of the Yellow and Blue Poison Dart Frog is classified as least concern.
Threats
- The yellow and blue poison dart frog’s natural predators are unknown, mainly due to their anti-predatory adaptations in the wild. Their bright yellow and blue skin serves as a warning to predators not to eat the frog. Their skin also features a poisonous chemical that is capable of paralyzing or even killing potential predators.
- As with many species in rainforest areas, habitat loss and human interference pose many problems to this amphibian species. Controlled fires to clear space for farmland is one example of the direct damages human interactions can have. Through habitat loss and their role in the illegal pet trade, this species has become one of the most threatened in the poison dart frog family.
Facts about Yellow and Blue Poison Dart Frog
Class:
Amphibia (frogs, salamanders, and carcilians)Order:
Anura (frogs)Family:
Dendrobatidae (poison-dart frogs, dart-poison frogs, dendrobatid frogs, dendrobatids, poison frogs)Genus:
Dendrobates (poison dart frogs)Species:
Dendrobates tinctorius (yellow and blue poison dart frog)Life Span:
4 – 6 years years (wild) / 10 – 12 years (zoo)Size:
Male: 1.57 inches (4 cm) / Female: 1.77 inches (4.5 cm)Weight:
0.1 ounce (3 g)
Fun Facts
- The spot pattern on each frog is different, like your fingerprints! Their coloration serves as a warning to predators not to eat them. The toxins in their skin are capable of paralyzing or even killing potential predators.
- Their skin remains sticky from mucus secretions which helps to hold moisture in and enables tadpoles to take hold when they are carried from the egg-site to their new aquatic home.
- Males have larger toe-tips, specifically those on the second, third, and fourth digits. In addition, these toe-tips are heart-shaped in males and round in females.