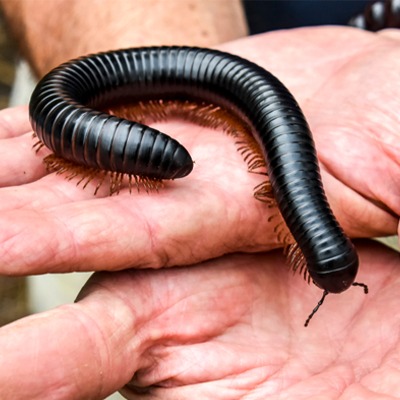

About Giant African Millipede
The giant African millipede has 300 to 400 legs. This millipede has weak jaws and cannot deliver a good bite. As a defense, it coils into a ball and secretes a foul fluid from its pores. Instead of breathing with lungs like mammals, millipedes breathe through tiny pore-like holes located down the length of their body, called spiracles. Because of this special breathing adaptation, if a millipede gets too wet, it could potentially drown.
Habitat
The giant African millipede lives in the rainforests of subtropical western Africa. Giant African millipedes love warm, dark places on the rainforest floor. The most common hiding places for this creature are burrows where they can curl up and hide, preferably near rotting wood.
Diet
They are detritivores, meaning they feed on dead and decaying organic (plant) matter within their habitat.
Family Life
Communication is important! Giant African millipedes have poor eyesight, so their sense of touch seems to play an important role. They can feel with their antennae and their legs, and can sometimes communicate by scent as well. When the time comes to reproduce, a male giant African millipede will wind around a female millipede. A few weeks later, the female will lay hundreds of eggs in a hole in the ground. Once a millipede hatches, it is on its own. There is no parental involvement, and it’s up to the newborn millipede to find food and shelter.
Conservation Status
The conservation status of the Giant African Millipede is classified as least concern.
Threats
- Not much is known about the giant African millipede and its conservation. Millipedes play a positive role in home gardens and residences, as they do not bite, sting, or eat food, fabric, or wood.
- Like many other insects, the millipede can be killed on site by humans, as there is a tendency to kill smaller insects that crawl.
Facts about Giant African Millipede
Class:
Diplopoda (Millipedes)Order:
Spirostreptida (long, cylindrical millipedes)Family:
SpirostreptidaeGenus:
ArchispirostreptusSpecies:
Archispirostreptus gigas (giant African millipede)Life Span:
5 – 7 yearsSize:
4 – 12 inches (10 – 30 cm)Weight:
Fun Facts
- Giant African millipedes can smell and taste with all parts of their body!
- Based on fossil records, scientists discovered that millipedes were one of the first animals to colonize land.
- Millipedes are decomposers, so their waste becomes new soil for the rainforest.