
About Reticulated Glass Frog
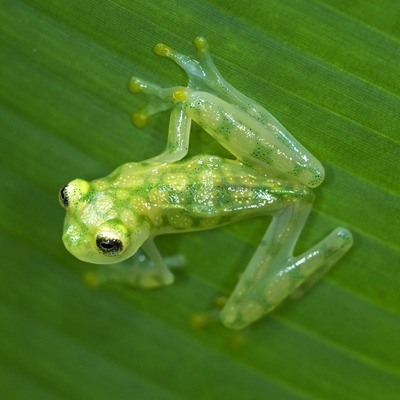
A transparent frog? As with many other glass frogs, the reticulated glass frog’s body is transparent. Their heart is visible from the outside of their bodies by a red color on their chests. The body also features yellow round spots and black dots on their light green skin. The nocturnal creatures are exceptional climbers, mainly due to their extensively webbed toes which help them get a grip on slippery branches.
Habitat
This species resides primarily in Central and South America, as it can be found in central Costa Rica, Ecuador, Colombia, and Panama. Their habitat is typically wet lowland forests, usually near streams or rivers.
Diet
Similar to its red-eye leaf frog friend, the reticulated glass frog is a carnivore. Their diet is mainly small insects like crickets, moths, flies, spiders, and even other smaller frogs.
Family Life
Male glass frogs are highly territorial throughout the wet season. Territories are made by using certain calls, like squeaking noises, to establish a new territory or to defend an established area. Females typically lay about 35 eggs on the underside of leaves hanging over streams or small rivers. The male guards the eggs both at night and during the day. The male frog will also engage in hydric brooding, which is when the male will lay his body over the eggs to further protect the eggs from intruders like wasps.
Conservation Status
The conservation status of the Reticulated Glass Frog is classified as least concern.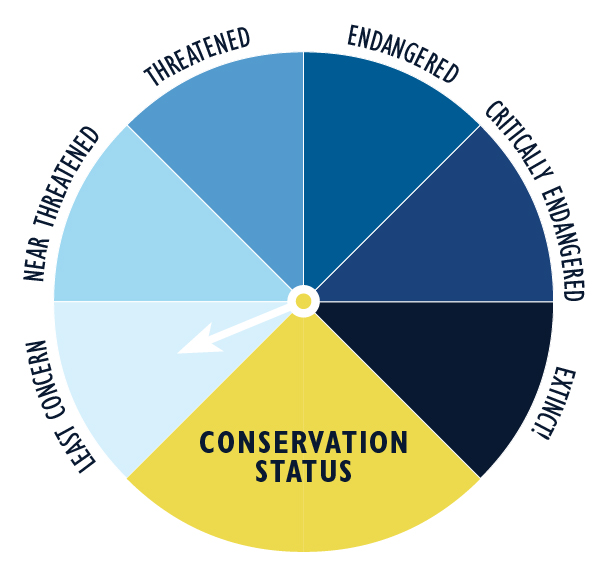
Threats
- Similar to other species living in the rainforest, habitat loss and deforestation play a major role in the overall stability of this species.
- Human interactions like intensified agriculture, grazing, and urbanization around the frog’s habitat have led to a steady decline in their population numbers over time.
- One of the most dangerous natural predators to the reticulated glass frog is the wasp. As tadpoles, the frogs are in an extremely vulnerable position and can be carried away by wasps or other flying insects for food. Snakes, birds, and some smaller mammals will target the reticulated glass frog as well.
Facts about Reticulated Glass Frog
Class:
Amphibia (amphibian)Order:
Anura (frog)Family:
Centrolenidae (glass frogs)Genus:
Hyalinobatrachium (glass frog)Species:
Hyalinobatrachium valerioi (reticulated glass frog)Life Span:
10 – 14 yearsSize:
Male: 0.7 – 0.9 inches (19.5 – 24 mm) / female: 0.9 – 1 inches (22.5 – 26 mm)Weight:
0.2 – 0.5 ounces (5 – 14 g)
Fun Facts
- Quite the disguise! The yellow and green spots on the frog’s body are able to mimic the color pattern of a clutch (or group) of eggs, allowing the frog and eggs to blend into the surrounding leaves where the male guards against predators.
- Males have been seen guarding up to seven different clutches of eggs on the underside of a single leaf.
- Reticulated glass frogs will sometimes eat their young!